Posts Tagged bash
Monitor s3sync with Zabbix
s3sync is a ruby program that easily transfers directories between a local directory and an S3 bucket:prefix. It behaves somewhat, but not precisely, like the rsync program.
I am using this tool to automatically backup the important data from Debian servers to Amazon S3. I am not going to explain here how to install s3sync as it is not the purpose of this article. However, you can read this very useful article from John Eberly’s blog: How I automated my backups to Amazon S3 using s3sync.
If you followed the steps from John Eberly’s post, you should have an upload.sh script and a crontab job which executes this script periodically.
From this point, here is what you need to do to monitor the success of the synchronisation with Zabbix:
- Add the following code at the end of your
upload.shscript:# print the exit code RETVAL=$? [ $RETVAL -eq 0 ] && echo "Synchronization succeed" [ $RETVAL -ne 0 ] && echo "Synchronization failed"
- Log the output of the cron script as follow:
30 2 * * sun /path/to/upload.sh > /var/log/s3sync.log 2>&1
- On Zabbix, create a new item which will check the existence of the sentence “Synchronization failed” in the file
/var/log/s3sync.log:
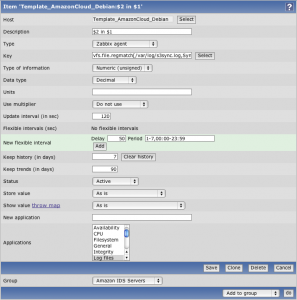
Item key:vfs.file.regmatch[/var/log/s3sync.log,Synchronization failed]
- Still on Zabbix, define a new trigger for the previously created item:
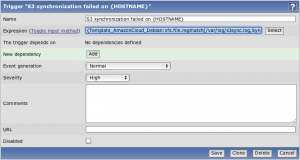
Trigger expression:{Template_AmazonCloud_Debian:vfs.file.regmatch[/var/log/s3sync.log,Synchronization failed].last(0)}=1
With these few steps, you should now receive Zabbix alerts when a backup on S3 fails. 🙂
Refresh GeoIP automatically
GeoIP is a very useful tool provided by MaxMind. It can determine which country, region, city, postal code, and area code the visitor is coming from in real-time. For more information, visit MaxMind website.
This tool is also coming with an Apache module allowing to redirect users depending on their location. For example, we could redirect all users from France to the French home page of a multi-language website, or we could block the traffic to users from a specific country.
To install this module on a Debian server, you simply need to run the following command:
apt-get install libapache2-mod-geoip
But, how does this module work? How does it know where the user comes from? 😯
It is actually quite simple: GeoIP is using a mapping file of IP address by country. On Debian, this file is stored in the folder /usr/share/GeoIP and is named GeoIP.dat.
However, the IP addresses are something which change all the time. So this file will get out-of-date very quickly. This is why MaxMind provides an updated file at the beginning of each month for free. To read the installation instructions, please click the following link: http://www.maxmind.com/app/installation
This is good and well, but who will remember or even have the time to update this file every month? And imagine if you have to do this on hundreds of servers?
The solution is to use a shell script which will download, extract and install the updated GeoIP file automatically once a month:
#!/bin/sh # Go in the GeoIP folder cd /usr/share/GeoIP # Remove the previous GeoIP file (if present) rm GeoIP.dat.gz # Download the new GeoIP file wget http://geolite.maxmind.com/download/geoip/database/GeoLiteCountry/GeoIP.dat.gz # Remove the previous GeoIP backup file rm GeoIP.dat.bak # Backup the existing GeoIP file mv GeoIP.dat GeoIP.dat.bak # Extract the new GeoIP file gunzip GeoIP.dat.gz # Change the permission of the GeoIP file chmod 644 GeoIP.dat # Reload Apache service apache2 reload
You can place this file in your root folder and set up the following crontab job:
0 0 3 * * /root/update_geoip.sh
This will execute the script automatically on the third day of every month.
run-parts gives an exec format error
I got a problem the other day with a Linux script I made.
Basically, the script was working perfectly fine if I executed it directly from the command line but whenever I tried to run it with run-parts it failed!
This is the error message it returned:
%prompt> run-parts --report /etc/cron.daily /etc/cron.daily/myscript: run-parts: failed to exec /etc/cron.daily/myscript: Exec format error run-parts: /etc/cron.daily/myscript exited with return code 1 %prompt>
Actually, the answer of this problem is quite simple! 🙂
I simply forgot the shebang on the first line of the script…
So, if you get the same error than me, make sure you have the following line at the beginning of your script:
#!/bin/sh
Redmine 1.1.3 on HostMonster
Did you guys ever hear about Redmine? It is an open source project management web application written using Ruby on Rails framework. I already used it in the past and it is quite powerful!
I wanted to install the last version (1.1.3) on my HostMonster account. I would lie if I say that it has been easy… However, after a few try and some help from the HostMonster support, I finally got it to work. 🙂
These instructions are basically a copy of the ones I found on GetTaskDone but updated with additional steps (in red):
- Create MySQL Database and Username
Login to CPanel and click on MySQL Database Wizard, it will prompt you for database name, then ask you to make a user, make sure you GRANT ALL privileges. Remember these database details, we will use them later. - Create a Sub-Domain
For the purposes of this tutorial, name it redmine, point this sub domain to ~/public_html/redmine.
Do NOT copy any files into this directory, we will be deleting it later. - Make sure you have the right version of Rails installed
In case it is different from what you need you can install a specific Rails version on your machine by running:%prompt> gem install rails -v=2.3.5
- Create RoR directory
It is not recommended that you put your RoR apps within the ~/public_html directory, as users would be able to see the rb files. So we are going to create a rails directory.%prompt> cd ~ %prompt> mkdir rails
- Create Rails App
You create a rails app on HostMonster just like you would on your system, by using the rails command. We are creating the rails project inside of the rails directory.%prompt> cd rails %prompt> rails -D redmine
We need -D to let rails know that we want custom dispatch.rb, dispatch.cgi and dispatch.fcgi files for later steps.
- Create a Sym-Link for Sub-Domain
Since the HostMonster interface won’t let you select a directory outside of public_html, we are going to create a symbolic link from the ~/public_html/redmine folder to ~/rails/redmine. To do this we will be deleting the ~/public_html/redmine directory. The symbolic link will recreate it.%prompt> cd ~/public_html %prompt> rm -R redmine %prompt> ln -s ~/rails/redmine/public redmine
Please note the space between ~/rails/redmine/public and redmine This command says create a new folder named redmine that points to ~/rails/redmine/public
- Do a Smoke-Test
Goto subdomain.yourdomain.com, you should see the default rails welcome page. This is fine, this is what you should see right now. - Prepare Redmine
Download the latest final release of Redmine (it’s 1.1.3 now). Extract this to your desktop, you should now have a folder name redmine on your desktop. Login to your CPanel and goto File Manager. You’ll want to navigate to ~/rails/redmine/public, you’ll want to download the following files and put them in your local copy of redmine. Which should be ~/Desktop/redmine/public. Download dispatch.rb, dispatch.cgi and dispatch.fcgi.
Now edit your database.yml file with the database, username and password you created in step one. You only have to change those three values for production and development configurations. To do so copy config/database.yml.example into config/database.yml and edit the latter. Comment out all the rest lines.
Now inside of your local redmine folder select all the files and folders and right click and select ‘Compress all the items…’. What we are doing is uploading this archive, I seem to have problems every time I try to upload redmine file by file. - Upload Redmine
If you don’t have File Manager open still then login to CPanel and open it again. Navigate to your ~/rails/redmine folder and click the check boxes on all items and click delete. Now, upload your archive. Once it’s done uploading click on the archive in File Manager and hit extract. - Finish install
Now ssh into your server, you’re going to want to chmod 755 your ~/rails/redmine/public folder.%prompt> cd ~/rails/redmine %prompt> chmod 755 public
Next, you must create a custom .htaccess file for Apache to handle this directory properly. First remove any .htaccess file that may already be in the ~/rails/redmine/public directory.
%prompt> cd public %prompt> rm .htaccess
Download file from here: http://www.gettaskdone.com/redmine-htaccess/htaccess.txt into ~/rails/redmine/public directory and save it as .htaccess.
Best way to do this is by typing following set of commands:%prompt> cd ~/rails/redmine/public %prompt> wget http://www.gettaskdone.com/redmine-htaccess/htaccess.txt %prompt> mv htaccess.txt .htaccess
- Edit Rakefile
RubyGems 1.6.x is incompatible with the bundled rails 2.3.5. It’s documented in the RubyGems release notes that “RubyGems no longer requires ‘thread’. Rails < 3 will need to addrequire ‘thread’to their applications.”
So we need to addrequire 'thread'to the Rakefile after the linerequire 'rake/rdoctask'. - Generate a session store secret
This is required on the trunk version of Redmine at r2493 or above and the released 0.8.7 version or above.
Redmine stores session data in cookies by default, which requires a secret to be generated. This can be done by running:%prompt> cd ~/rails/redmine %prompt> RAILS_ENV=production rake config/initializers/session_store.rb
- Edit config/enviroment.rb
Insert the following code between the bootstrap and the initialize sections in the config/enviroment.rb file:if Gem::VERSION >= "1.3.6" module Rails class GemDependency def requirement r = super (r == Gem::Requirement.default) ? nil : r end end end end - Setup Database
We have to give redmine its database structure and default values.%prompt> cd ~/rails/redmine %prompt> RAILS_ENV=production rake db:migrate
- Insert default configuration data in database
Run the following command:%prompt> RAILS_ENV=production rake redmine:load_default_data
This step is optional but highly recommended, as you can define your own configuration from scratch. It will load default roles, trackers, statuses, workflows and enumerations.
- Rename the ‘vendor/rails’ folder
Run the following command:%prompt> mv vendor/rails vendor/rails.old
The vendor directory generally takes precedence over the other locations where Rails looks for libraries, and if it contains different versions of gems or other items, it can cause conflicts.
For your information, these are the links I used to write this article:
ntpd process on D-Link DNS-313
During the configuration of a D-Link DNS-313 which is basically a NAS (Network-Attached Storage), I got a serious but easy-to-fix problem. 🙂
In order to get access to the box by command line, I installed the Fonz fun_plug. I then wanted to automatically synchronise the internal time with some NTP Pool Time Servers. But, for some reason, the version of the ntpd process provided with fun_plug is completely freezing the NAS. I wasn’t able to find the root cause of it, trust me, I tried everything I could think of!
Please also note that the same process is working perfectly fine on his brother, the D-Link DNS-323. As I said, I can’t explain why… 🙄
But there is a good news! The ntpd process is actually part of the D-Link DNS-313 firmware. And it is working fine! 😀 After double-checking, this process is however NOT part of the D-Link DNS-323 firmware. Why is that? Maybe D-Link got complaints from DNS-313 users and fixed it? Who knows…
Anyway, in order to get the ntpd process to work on the D-Link DNS-313, you need to replace the content of your ntpd startup script (/ffp/start/ntpd.sh) by the one below:
#!/ffp/bin/sh
# PROVIDE: ntpd
# REQUIRE: SERVERS
# BEFORE: LOGIN
. /ffp/etc/ffp.subr
name="ntpd"
command="/usr/sbin/ntpd"
ntpd_flags="-f /ffp/etc/ntpd.conf"
required_files="/ffp/etc/ntpd.conf"
start_cmd="ntpd_start"
ntpd_start()
{
# remove rtc and daylight cron jobs
crontab -l | grep -vw '/usr/sbin/daylight' | grep -vw '/usr/sbin/rtc' | crontab -
proc_start $command
}
run_rc_command "$1"

